IPBES
The FRB hosts the scientific secretariat of the French committee for IPBES, the intergovernmental science and policy platform on biodiversity and ecosystem services. It thus actively contributes to promoting IPBES’ work at the national level and encourages ministries, researchers, and stakeholders to participate in the report development processes.

The role of the FRB is to mobilize French expertise in the work of IPBES, and to encourage dialogue between science and policy by providing support to French representatives at IPBES for the preparation and participation in plenary sessions.
Particular attention is also paid to relaying the ongoing work and results of the platform with the aim of: transferring knowledge; encouraging the mobilization of society (in particular through the FRB’s Stakeholder Assembly (SSA) and establishing a link between the work of IPBES and other relevant initiatives.
The FRB regularly organizes the IPBES-IPCC meetings, an event that aims to bring together research communities, public and private decision-makers and stakeholders on biodiversity and climate issues at an international level:
IPBES is an independent intergovernmental body that provides policymakers with:
- objective scientific assessments of the state of knowledge (academic and non-academic) on biodiversity, ecosystems and their benefits for individuals,
- tools and methods to protect and sustainably use these vital natural resources.
Key figures and dates
- 2012 : Creation of IPBES by 94 governments, under the aegis of several United Nations programs and organizations.
- 152 Member States as of March 21, 2025.
- More than 1000 experts mobilized.
- Hundreds of representatives from the business world, civil society and other stakeholders.
IPBES objectives
“Strengthening the science-policy interface for biodiversity and ecosystem services with the aim of ensuring the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity, the long-term well-being of humanity and sustainable development” : one of the statutory objectives of IPBES
Achieving this objective relies on four complementary and closely linked functions:
- catalyze the production of new knowledge;
- assess existing knowledge;
- support the formulation and implementation of policies;
- strengthen the capabilities required to achieve its objective.
The platform relies heavily on the involvement of scientific experts, stakeholders, and policymakers in its work. IPBES’s methodology is unique in that it integrates scientific, local, and sectoral knowledge equally in the generation of knowledge: stakeholders and experts, including academic experts, are involved on an equal footing.
Les évaluations de l’Ipbes
In concrete terms, the IPBES work program consists mainly of carrying out assessments of the state of knowledge on biodiversity and ecosystem services (well-shared and therefore established knowledge, more uncertain knowledge and knowledge gaps).
These assessments can be thematic (assessment of pollinators and pollination services, etc.), geographical (assessment focused on Europe and Central Asia, etc.), or methodological (assessment of the multiple values of nature, etc.). They actively involve 100 to 200 international and multidisciplinary experts working on:
- a review of academic and grey literature, taking into account the knowledge of local and indigenous populations;
- a summary for decision-makers , approved at the end of the process by all the member states of the Platform.
In its Guide for the Production of Assessments ( IPBES Guide on the Production of Assessments, 2018 ), IPBES specifies that, in order to produce “credible, legitimate and relevant” assessments , these must “involve governments and other stakeholders in their initiation, framing, review and adoption”.
Typically, the production of an evaluation – consisting of a scientific report and a summary for decision-makers – follows this path, from the adoption of the topic to the adoption of the evaluation:
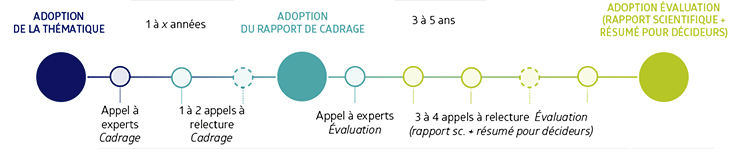
Experts, scientists and stakeholders have the opportunity to be involved from the outset in the drafting or to provide opinions, observations, comments during various phases of the production of the assessments.
· Biodiversity and Transformative Change
More informations |
· Nexus (links between biodiversity, water, food, health and energy)
More informations
· Invasive alien species, 2023
· Conceptualizations of the different values of nature and its benefits, 2022
Summary for policymakers
· Sustainable use of wild species, 2022
· Global Assessment of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, 2019
· Regional assessments of biodiversity and ecosystem services, 2018
Summary for policymakers
· Land degradation and restoration, 2018
· Pollinators, pollination and food production, 2016
· Scenarios and models of biodiversity and ecosystem services, 2016
Summary for policymakers
· Impacts of and dependencies of businesses on biodiversity
· 2nd global assessment of biodiversity and ecosystem services
· Biodiversity monitoring systems
Please note: All IPBES reports are available in English. For each assessment, a summary for policymakers is available in French.

Vous souhaitez être destinataire des informations FRB liées à l’Ipbes ?
Inscrivez-vous aux alertes :